Litecoin – The Digital Silver
In the following blog, we will introduce you to another cryptoasset from our dynamic portfolio – Litecoin. Litecoin is a constant member of our Fumbi Index Portfolio that came about as an alternative cryptocurrency with fast and cheap peer-to-peer transactions that are not controlled by any central authority.

Historical Development of Litecoin
The beginnings of Litecoin go back to 2011 when its founder Charlie Lee, a former Google engineer and MIT graduate, decided to create the first ‘successful’ alternative cryptocurrency by copying and modifying Bitcoin’s source code.
Back when Litecoin was created, only eight altcoins existed, and seven of them were forks. Forks are projects that largely took over Bitcoin’s source code and made a few changes. Even though Litecoin wasn’t the first alternative cryptocurrency to copy and modify Bitcoin’s source code, it’s historically one of the most successful and well-known altcoins. Thus it earned the status of a “digital silver”.
The main idea behind Litecoin was to create an alternative that provides cheaper and faster transactions than Bitcoin to increase the effectiveness of the use of cryptocurrencies for regular transactions. Litecoin deviated from bitcoin to test new innovations and possibilities for the application of cryptocurrencies.
What is Litecoin?
Litecoin is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency that allows for immediate payments to anyone anywhere in the world with almost zero expenses. Like Bitcoin, Litecoin is a decentralised cryptocurrency founded on a global payment network with open source code that isn’t controlled by any central organ.
Initially, Litecoin was a strong competitor of Bitcoin, mainly due to its fast and cheap transactions. However, because of the growing number of alternative cryptocurrencies, Litecoin’s popularity eventually started to decline.
Elemental Differences Between Bitcoin and Litecoin
Like Bitcoin, Litecoin uses a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism to verify blockchain transactions. However, due to certain modifications, this system is considered a ‘lighter’ and faster version of Bitcoin.
The key difference between Litecoin and Bitcoin is that Litecoin uses a mining algorithm called Scrypt PoW, which allows for shorter transaction times. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 PoW algorithm.
The Scrypt PoW mining algorithm initially focused on lowering the efficiency of specialised miming equipment but was ultimately unsuccessful. Though it’s still possible to mine Litecoin even with home mining equipment, the industry is dominated by large scale Litecoin miners.
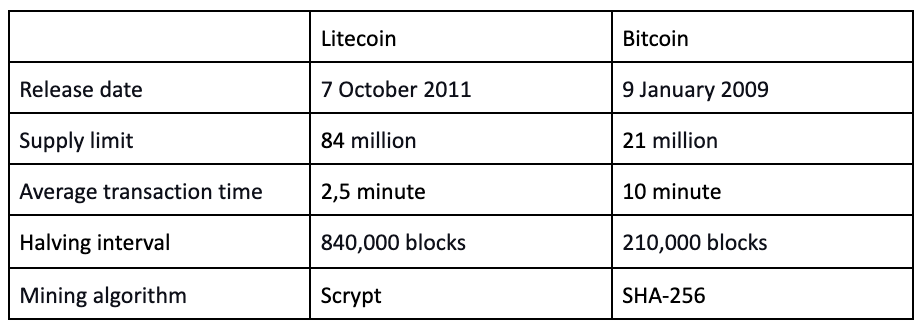
Litecoin generates a new blog approximately every 2.5 minutes – about four times faster than bitcoin, which generates a new block around every 10 minutes. It’s directly proportional to the litecoin supply that is four times higher than bitcoin. While bitcoin’s limit is 21 million BTC, the litecoin is capped at 84 million LTC. The following table characterises the basic differences between Litecoin and Bitcoin:
Litecoin Halving
New litecoins are created through the mining process when miners add new transactions into the blocks. The miner that manages to verify a block gets a certain amount of litecoins as a reward for their effort. The amount consists of a set number of new Litecoins and transactional fees included in the block.
The Litecoin network’s base reward is halved every 840,000 mined blocks. Considering the average block mining speed of 2.5 minutes, approximately 210,000 blocks get mined per year. That means halving in the Litecoin network takes place about every four years.
The last halving within the Litecoin network happened on 5 August 2019, when the base block reward (so-called coinbase) got halved from 25 LCT to 12.5 LTC per block. Next halving is expected around 23 August 2023, when the block reward will drop from 12.5 LTC to 6.25 LTC.
The idea behind halving is a gradual decrease in the accumulation of litecoins. In traditional financial markets, the decreasing offer of an asset with a constant or growing demand leads to growth of value because the rarity of the asset is increasing.
Litecoin SegWit
Segregated Witness is a blockchain protocol upgrade proposed as a solution for an issue with Bitcoin scaling. The need for a SegWit was caused by a 1MB block size limit on the bitcoin blockchain. With the increased use of the network, the blocks began to fill up fast, slowing transactions and increasing transaction fees.
Many miners initially criticised SegWit as a dangerous upgrade for the bitcoin blockchain. Some even believed it might cause a complete collapse of Bitcoin. Of course, every blockchain upgrade poses risks, such as an incorrect source code. If the code wasn’t properly checked and tested, it could disrupt the network.
Litecoin was the first cryptocurrency that implemented SegWit within its platform. As a result, Litecoin proved that the code works as it’s supposed to. The SegWit implementation drew considerable attention to Litecoin in the crypto community. It even led to considerations of using Litecoin as a “canary network” for Bitcoin where could be tested various improvements for Bitcoin’s future development. Either way, Litecoin provided invaluable help to the bitcoin community by showing that there is no need to be afraid of SegWit, and the upgrade works as it’s supposed to.
Lightning network
The 2017 Litecoin SegWit actualisation prepared an excellent soil for Lighting Network implementation on the Litecoin network.
Lightning Network is an off-chain system of payment channels run by smart contracts and designed to simplify direct trade between users.
The idea of Lightning Network is that the payment channels where transactions take place are outside of Litecoin’s main chain. That makes it possible to perform transactions between subjects that don’t trust each other without the necessity to stress the main network.
The payment channels are usually focused on smaller transactions, such as payments for a coffee or lunch. After opening a channel, for example, between the customer and the cafe, both parties can immediately exchange an unlimited amount with minimal transaction fees.
Opening a channel means a single transaction on the main chain. Then all transactions through the channel are recorded off-chain until one of the parties decides to close the channel. Closing the channel means uniting all off-chain transactions under a single transaction written into the blockchain.
Furthermore, the Lightning Network implementation introduced so-called Atomic Swaps that allow the trader to exchange bitcoin for an equivalent amount of Litecoins. This added considerably to the increase in interoperability of these two very similar networks.
Litecoin Goals
Litecoin is a form of digital money that both individuals and institutions can use to purchase assets and transfer resources between economic subjects. The main advantage of using litecoin is that subjects can perform cheap and fast transactions without the necessity of interaction with the provider, such as a bank or centralised payment gate.
Presently, Litecoin isn’t receiving the attention it deserves. However, once cryptocurrencies reach a critical number of users and become a truly accepted payment method, maybe it will be Litecoin that becomes the standard cryptocurrency of a new digital sphere.
INVEST WITH FUMBIIf you are considering investing in cryptocurrencies, Fumbi is here for you. Our algorithm administered portfolio precisely mirrors movements on the crypto market.
The Fumbi company is the first of its kind because it offers cryptocurrencies to the general public and even at minimal deposits. Investing in cryptocurrencies through Fumbi is very simple and minimises risks.
You can start with a deposit from €50
*Did you come across a term you didn’t understand? Don’t worry. You can find all essential terms regarding cryptocurrencies in our Fumbi Dictionary.

 3 min •
3 min •



