Polkadot – Decentralised Web 3.0
This series will introduce you to all cryptocurrencies that are a part of our dynamic portfolio. The following article will introduce you to Polkadot – a cryptocurrency whose popularity is growing each day, especially due to its great innovative potential and the possibility of becoming a true and respected competitor of Ethereum.

History
Behind Polkadot stands a trio of founders headed by Dr Gavin Wood, one of the important figures of Ethereum’s early stages. Wood was not only a co-founder of Ethereum but also its CTO and lead developer. He invented the Solidity language, which is still used to write smart contracts.
The whitepaper of this cryptocurrency was published back in October 2016. However, the company didn’t organise a public offering of tokens until 2017 during the ICO fewer. The founders managed to raise an incredible $144.63 million via the ICO (Initial Coin Offering).
In terms of the amount of capital raised in the initial phase, this is one of the most successful projects in history. Subsequently, two more investment rounds took place in 2019 and 2020, where investors managed to raise an additional $43 million, which enabled the official launch of Polkadot. The Genesis block network was established on 26 May 2020, when the network was officially launched.
What Is Polkadot?
Polkadot is a network protocol that allows the transmission of any data (not only tokens) through blockchains. It is a new generation of blockchain that enables cross-communication (interoperability) by connecting multiple blockchains into a single network. The basis of the whole ecosystem is the optimisation of a solution in which several blockchains will be able to operate on a single common foundation. At the same time, each of these blockchains will be able to focus on solving a specific problem for which it will be optimised.
The Polkadot cryptocurrency ecosystem is expanding every day as developers all over the world become increasingly aware of the benefits of this flexible, efficient, and secure network. Combining several specialised blockchains dedicated to solving a specific problem into one highly scalable interconnected network will enable each blockchain to reach its full potential.
On the Polkadot platform, projects no longer have to compete with each other. Blockchains in the Polkadot network can cooperate and prepare together for independence from the centralised world.
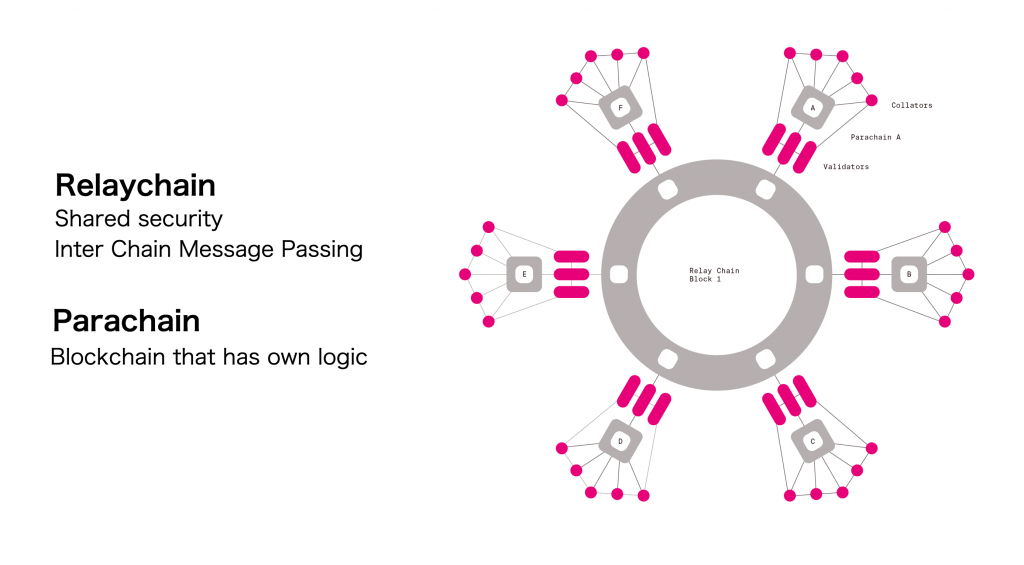
Relay Chain
The relay chain is the main chain of the Polkadot network. We can consider it a building block of the whole ecosystem. Polkadot uses the NPoS (Nominated Proof-of-stake) consensus mechanism. Therefore, all validators in the network stake DOT tokens directly through the Relay Chain and thus participate in its validation and security. Relay Chain enables fast real-time transactions throughout the network and is a kind of communication “node” between the parachains in the Polkadot network. However, the Relay Chain itself does not have the functionality of smart contracts.
Substrate Framework
An important functionality of the Polkadot network is the Substrate framework developed by Parity. Its task is to significantly simplify creating, deploying, upgrading and experimenting with different types of blockchains aimed at solving a specific problem.
Running your own blockchain was disproportionately difficult and costly in the past, and several projects failed on this issue. The Substrate framework’s main task is to facilitate the accompanying processes and enable decentralised applications developers to focus more on innovation and development than on building and maintaining the blockchain itself. Edgeware is an example of a project built on the Substrate framework.
Parachain and Parathreads
Parachains are independent blockchains that run on Relay Chaine, providing various network-specific functions for the Polkadot network. Each parachain within the network may have a different function – one may provide an environment for smart contracts, another may provide payments between blockchains, for example, through its own stablecoins, and another may be security and anonymity oriented. Thus, different parachains may arise on Polkadot, and each will deal with its own specific problem.
Parachain usually has its own management and team of developers. Any parachain that wants to be part of the Relay Chain must first win the auction in the Polkadot ecosystem. The winner of the auction will always be the parachain with the largest number of DOT tokens in the given auction.
The trick is that the project must either purchase the tokens (which positively affects the price) or rent them from DOT community users who see potential in the project. The reward for the lessors can then be an interest income or newly created tokens of that particular winning parachain.
Parathreads work on a very similar principle to parachains. The main difference between them lies in their economic-operational nature. Parathreads are more advantageous for projects and solutions that don’t require a constant connection to the network. For example, Parathread can be used for a one-time network connection to obtain the necessary data.
What Is the Purpose of Bridges?
The basic technology of interoperability of each blockchain is the construction of the so-called bridges. An important part of Polkadot is also the focus on possible communication with blockchains that operate outside the Polkadot ecosystem. Polkadot tries to solve this problem by implementing parachains focused on interoperability solutions. The essence of the whole dilemma is for the Polkadot network to be able to communicate with other blockchains in the future, such as Ethereum or Cardano.
The Forkless Upgrade Technology
The “forkless upgrade” technology is one of the most significant technological changes that Polkadot brings to the world of cryptocurrencies. It is a technology that eliminates the need for forks through a special governance model built directly into the Relay Chain and implemented by a transparent network mechanism.
Under this mechanism, network participants will be able to decide on any changes regarding the development of this cryptocurrency. Also, each of the blockchains operating on Polkadot will have the opportunity to create their own governance voting model, allowing each blockchain to solve the problems through internal decision-making mechanism. Therefore, the entire network will not need to be forked.
Kusama and Polkadot
Kusama, also known as the “Polkadot Canary”, is a sister network of Polkadot built on the same principle as Polkadot itself. While Polkadot is based on flawlessness, Kusama acts as a quasi- “testnet” of the Polkadot network.

Kusama provides an optimised environment for testing innovations and changes before their direct implementation on Polkadot itself. It also acts as a blockchain to which various interesting projects can join, as is the case with Polkadot. Kusama may be a cheaper and more convenient alternative for individual parachains in the future.
DOT Token
DOT is a native Polkadot token. For example, ETH is a native Ethereum token, or ADA is a native Cardano token. The Polkadot token performs three basic functions:
- Governance : DOT token holders have full control over the network protocol and can vote on protocol’s future. They can decide, for example, the dynamics of auctions or the amount of network fees.
- Staking : Because Polkadot uses Proof-of-Stake as a consensus mechanism, the DOT token is held by various groups of investors who want to be part of the network and thus participate in development and decision-making. Investors can stake the DOT tokens and collect rewards for it.
- Bonding : DOT tokens will be used for adding new parachains. If a new parachain joins the Polkadot ecosystem, its DOT tokens will be locked until the parachain is no longer used.
DOT Token’s Inflationary Character
Polkadot tokens are not deflationary. This means that they do not have a predetermined amount in circulation such as Bitcoin, Litecoin, or Cardano. From this point of view, we can classify Polkadot into inflationary cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum, Solana, or IOTA. Current token inflation is at the level of 10% per year, while staking of tokens brings validators an average annual yield of up to 13%.
Current Stage: Polkadot Rollout and Slot Auctions
Polkadot is currently running slot auctions as new projects are securing their slots. The first five parachains went live in December 2021: Acala, Moonbeam, Parallel Finance, Astar, and Clover. They were joined by another six in March, bringing their total to 11. This time next year, Polkadot will be home to over 40 individual blockchains. Presently, the Relay Chain can support anywhere from 100 to 250 blockchains, so there is plenty of room for the many projects waiting to join its ecosystem. Kusama already has over 30 parachains up and running. Gavin Wood’s vision of the vast interconnected network of cooperating blockchains is becoming a reality.
Invest With Fumbi Today
If you are considering investing in cryptocurrencies, Fumbi is here for you. Our algorithm-administered portfolio accurately tracks the growth of the entire cryptocurrency market.
Fumbi is the first of its kind to offer cryptocurrencies to the general public, even at small deposits. Investing in cryptocurrencies through Fumbi is very easy and minimises risks. You can also invest in the cryptocurrency Polkadot individually through our Fumbi Custom product.
You can start with a deposit of just €50.
INVEST WITH FUMBIDid you come across a term you didn’t understand? Don’t worry. All essential terms regarding cryptocurrencies are in our Fumbi Dictionary.

 3 min •
3 min •



