Chainlink – Decentralised Oracle Network
The following article will introduce another cryptoasset from our dynamic portfolio – Chainlink. Chainlink is a decentralised Oracle network that plays an important role in the implementation of blockchain technology in the real world. The main goal of this network is to provide inputs from various external data sources to the blockchain.

History of Chainlink
The Chainlink network was founded in 2014 by Sergey Nazarov, a relatively well-known figure in the cryptoasset ecosystem. The original idea of this network was to create a centralised Oracle system that could verify incoming inputs from external sources. However, the idea gradually transformed into a decentralised Oracle network that communicates with smart contracts and verifies the authenticity and security of data from external sources.
The Chainlink network was officially launched in June 2017 under the leadership of the SmartContract company. A few months later, in September 2017, the project’s Whitepaper was published, describing the complex operation.
The Chainlink team sold native tokens through an initial coin offering (ICO) and managed to raise $32 million by selling 35% of their total token stock.
What is Chainlink?
Although blockchain performs the role of a decentralised, secure ledger for transactions in any network almost perfectly, its shortcomings are particularly evident in receiving information and data from outside the blockchain.
In practice, a massive amount of external factors and information affect events in all financial markets, including the cryptocurrency one. Chainlink deals precisely with the issue of security and authenticity of external data affecting the blockchain.
Chainlink is a decentralised blockchain network. In a way, it creates a bridge between the Oracles that provide blockchains with proven and secure inputs from the real world and smart contracts that operate on individual blockchain networks.
Each Oracle Chainlink network consists of multiple independent Oracle nodes that obtain data from multiple independent external data providers. These nodes then aggregate and merge the data into a single data point, which they then transmit to the blockchain so that the data can be used to make smart contracts work properly.
Oracles
Oracles are specific data channels that are necessary for most blockchains because blockchains cannot directly access external data sources outside their network. Oracles act as an entity that finds and verifies real-world data and sends this information to the blockchain. External data are often needed to execute a smart contract with predefined conditions.
Smart Contract Architecture
The Chainlink network architecture generally consists of three basic types of smart contracts:
- Order-Matching Contract – This contract assigns a “Service Level Agreement (SLA)” to Oracles with the best offer.
- Reputation Contract – Verifies the integrity of Oracle by reviewing its records. This includes factors such as the total number of requests completed, the average response time, and the amount of LINK cryptocurrency available to Oracle. Based on this, the contract evaluates and identifies dubious and unreliable nodes.
- Aggregating Contracts – Aggregating contracts collect data from Oracle and assign the most accurate results to each smart contract that needs it.
How Does Chainlink Work?
To ensure communication between blockchain-based smart contracts that provide various services and external data sources, Chainlink performs two basic types of operations: on-chain and off-chain. The overall data acquisition process consists of three steps.
- Step 1: Oracle Selection – An entity that needs to draw data from an external source proposes a contract called “Service Level Agreement (SLA)” that specifies a set of requirements and criteria the data must meet. Chainlink will then use this SLA to assign the applicant the most appropriate Oracle using a reputational contract that can provide the data based on its specifications. After setting and matching the parameters, the user confirms, sends the SLA, and inserts the Chainlink (LINK) cryptocurrency into the “Order-Matching Contract”.
- Step 2: Data reporting – In this step, Oracle actually connects with external data sources to obtain the data required in the SLA for a specific entity. The data collection from external systems takes place off-chain. The data is then processed and transformed by the individual Oracles into a form that can be sent back to the blockchain using the Chainlink service.
- Step 3: Result Aggregation – The last step in this process is to add up the results of the data collected through Oracles and return them to the aggregation contract. The Aggregation Contract takes over this data, assesses the validity and integrity of each, and returns the weighted score to the user using the sum of all data received into the client contract.
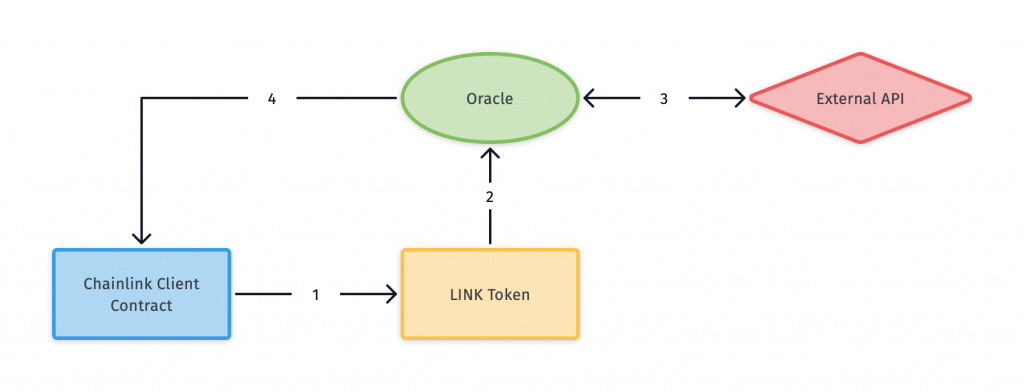
When performing these operations, Chainlink must also communicate with Oracles that operate off-chain, i.e. outside the Chainlink blockchain.
The entire off-chain architecture stands on two basic kinds of software:
- Chainlink Core – This is open-source software on which nodes with Oracles functionalities operate. Chainlink Core is responsible for reading newly submitted SLAs, redirecting them, and assigning them to the Chainlink Adapter.
- Chainlink Adapter – Acts as a bridge between the node and external data. The adapter can read and process data and write it to the blockchain.
As part of off-chain operations happens the actual collection of data and information from external systems and their transformation into a form that individual nodes can process and send back to the blockchain. The nodes are then rewarded in LINK tokens for performing these tasks.
Chainlink Ecosystem
Chainlink currently has a very strong market position due to several significant partnerships extending beyond the cryptoasset ecosystem. Chainlink’s strongest partners include:
- SWIFT – The cooperation between Chainlink and SWIFT is an important step towards integrating the LINK token into the traditional international banking system. LINK also has a good reputation in the mainstream thanks to this cooperation.
- Google Cloud – Chainlink and Google Cloud collaborate to make it easier for developers to develop technology by giving them access to cloud data on public blockchains through Oracle.
- Dapps Inc. – Chainlink and Dapps Inc. have announced a partnership that will enable users of Salesforce, a cloud-based business software, to obtain accurate, real-time data for smart contracts.
- Binance – Chainlink is helping Binance, the largest cryptocurrency exchange, share its crypto data with other blockchain platforms.
Chainlink also works with several blockchain networks, such as Cardano, PolkaDot, Polygon and Tezos.
Native Network Token – LINK
The native network token LINK is built directly into the network and is the only token that can be used to perform key network operations.
LINK originated as an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum network and went into circulation through an initial coin offer (ICO), during which up to 350,000,000 million tokens (35%) of the total 1,000,000,000 were sold. As LINK tokens are used as the currency on this platform, the more Chainlink’s services are used, the greater the demand for this asset.
LINK is used in the Chainlink network to pay individual network operators for their data acquisition services from external data sources, converting them into a blockchain readable format and delivering them to the blockchain.
As part of the innovation, the ERC677 interface is also implemented in the LINK token agreement. ERC677 is an extension of the ERC20 standard, which has all the advantages of ERC20 and, at the same time, addresses its limitations. It is more advanced and allows more functions. It is fully compatible with the ERC20 and Ethereum mainnet infrastructure and tools while offering lower transaction costs.
ERC677 offers a solution called transferAndCall, in which the user can send tokens to the contract, and the receiving contract can receive these tokens in one transaction.
Take Advantage of the Potential of This Cryptocurrency
Over the years, Chainlink has gained immense popularity among investors worldwide. As the market for cryptocurrencies and decentralised finance continues to evolve, the amount of financial capital is shifting to the functional, scalable, and secure networks of the new, innovative Web 3.0.
Many experts now consider Chainlink a relatively underrated cryptocurrency with great potential, working on several new technological improvements and tokenomics over 2022.
Chainlink is also an integral part of our Fumbi Index Portfolio. We perceive this cryptocurrency’s greatest potential in its usefulness and utilisation not only in the ecosystem of cryptocurrencies but also outside the sphere of cryptoassets. An example is cooperation with several companies from the traditional world, including Google, that use Chainlink to develop hybrid blockchain applications.
Invest With Fumbi Today
If you are considering investing in cryptocurrencies, Fumbi is here for you. Our algorithm-administered portfolio accurately tracks the growth of the entire cryptocurrency market.
Fumbi is the first of its kind to offer cryptocurrencies to the general public, even at small deposits. Investing in cryptocurrencies through Fumbi is very easy and minimises risks.
You can start with a deposit of just €50.
INVEST WITH FUMBIDid you come across a term you didn’t understand? Don’t worry. All essential terms regarding cryptocurrencies are in our Fumbi Dictionary.

 3 min •
3 min •



