Aave – Decentralised Loan System
The following blog will introduce you to another cryptoasset from our dynamic portfolio – the Aave protocol. Aave is a decentralised money market protocol that allows individual users to borrow money without the need for trust in another economic entity. Aave offers a wide range of cryptocurrencies with variable and stable interest rates.

History
The origins of the Aave protocol date back to 2017, when Finnish developer Stani Kulechov and his team of developers jointly launched the peer-to-peer lending platform ETHLend through an initial coin offering (ICO). The goal was to create a modern lending concept where users can borrow cryptocurrencies from each other.
Although ETHLend was a new and innovative idea in the world of finance, the platform and its $LEND token have declined since 2018 due to the bear market. The main reason for the collapse of this platform was the lack of liquidity caused by the massive outflow of capital from the market. Furthermore, the platform experienced increasing problems with matching supply and demand for loans due to declining liquidity.
Due to the bearish period in the cryptocurrency market, the ETHLend team developed the concept of their new product and, in 2020, launched an innovative decentralised protocol called Aave.
Kulechov himself later admitted that the arrival of the bear market was one of the best things that could have happened to him and his team. According to Kulechov, this was a sign and a “second chance” to rework the concept of decentralised loans in cryptocurrencies. This second chance led to the Aave Protocol, which is currently the largest protocol in decentralised finance.
What is Aave?
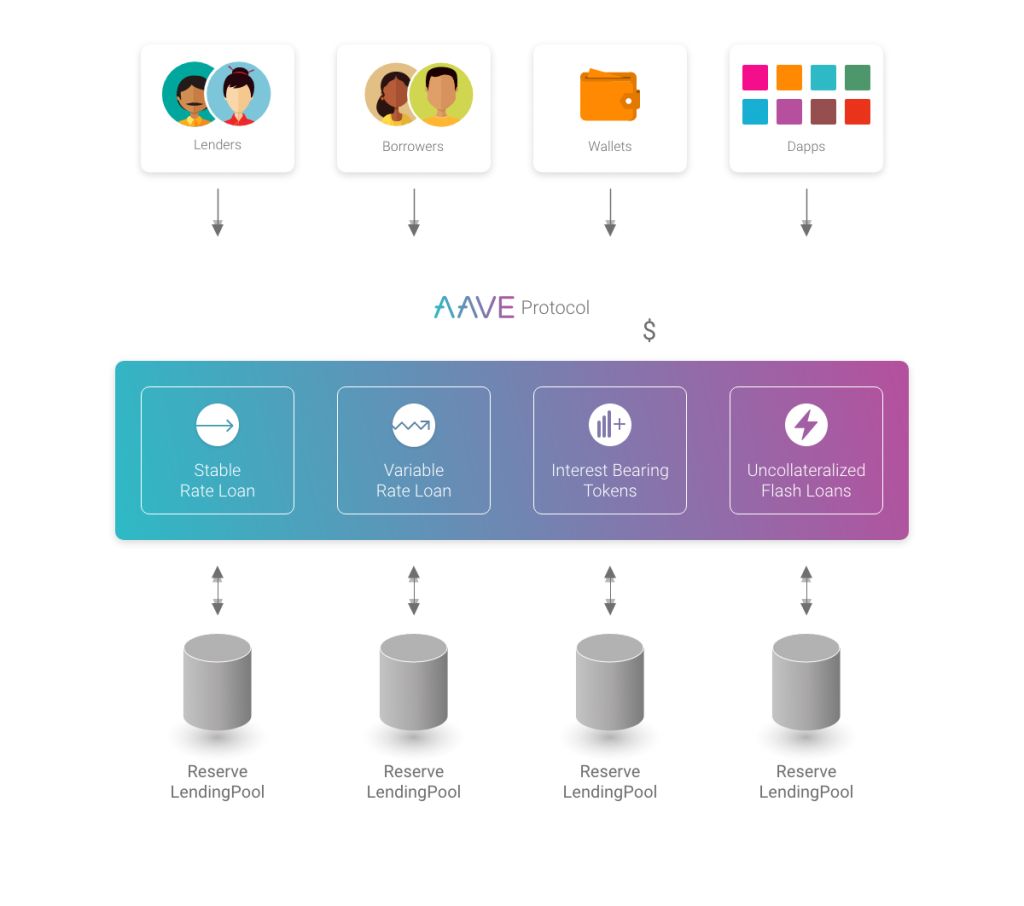
Aave is a money market based on the Ethereum blockchain. On one side, there are entities that lend their free funds and collect interest, and on the other side are the entities that borrow these funds at a certain, pre-arranged (fixed) or variable interest rate.
The new and improved Aave concept brought with it algorithmic loan processing. In practice, loans are obtained from liquidity pools instead of being individually matched to individual creditors and borrowers peer-to-peer.
Aave makes it easy to lend via stablecoins and various other altcoins. However, under the system of algorithmic loan pooling, borrowers must enter collateral in the protocol that is higher than the amount they borrow.
If a borrower applies for an Ether loan worth $10, he must enter collateral worth more than $10 in another cryptocurrency. To account for the volatility of crypto markets, the protocol has an Aave algorithm that automatically liquidates the debtor’s collateral if its value falls below a specified ratio. Each loan in the network is managed by a smart contract whose functionality and source code are verified by an independent third-party audit.
Key Features of Aave
- Open-source – The Aave protocol is open source. It means that anyone can see, use, or implement the original source code created by the Aave team.
- Non-Custodial – The Aave protocol is a non-custodial protocol, which means that the Aave platform itself never holds or otherwise owns your cryptoassets. Maintaining full ownership and control of your cryptoassets is an essential and key part of truly decentralised finance.
- Trustless – The Aave protocol allows you to borrow funds without having to trust another person or institution.
How Does Aave Work?
Using the Aave protocol, entities with free funds can collect passive interest on their digital assets.
Lenders can deposit their tokens in liquidity funds and receive secondary interest tokens, also known as aTokens. For example, if a user enters USDC into the stablecoin protocol, he collects a secondary token, aUSDC, in return. These secondary tokens are always issued upon deposit and liquidated when the original asset is withdrawn from the protocol. The aTokes are issued in a 1:1 ratio to the underlying asset, which the creditor enters in the protocol.
The interest earned through aTokens is variable and varies depending on the basic principle of the market mechanism – demand and supply. As creditors’ deposits operate in a “global liquidity market”, the interest rates naturally increase when demand for loans is high. The protocol seeks to attract liquidity providers with high interest rates to inject more capital. On the other hand, if there is excess liquidity in the pool, interest rates are low, which motivates entities to take a cheap loan.
The Aave protocol offers users two types of interest rates for both the lender and the borrower:
- Variable interest rates – An interest rate calculated algorithmically based on the demand and supply of assets deposited in a liquidity pool.
- Fixed interest rates – An interest rate that represents the 30-day interest average of an asset.
A key factor in decentralised loans through Aave is that the protocol does not require any personal identification. The protocol does not care about your credit history, does not deny you a loan if you have enough collateral, and does not take into account any ethnic, racial or other prejudices.
How to Borrow Through Aave
To borrow through the Aave protocol, it is first necessary to secure a loan with sufficient collateral. For decentralised loans, the amount locked must always be greater than the amount borrowed. For Aave, the loan amount is determined using the Loan-To-Value (LTV) indicator, which determines how much can be borrowed against the collateral provided. Currently, the loan amount ranges from 50% to 75% of locked collateral, depending on the asset.
For example, if a user wants to borrow Ethereum, which has an LTV of 75%, and locks in collateral worth 1 ETH, they can borrow a maximum of 0.75 ETH.
The guarantee of repayment of crypto loans is secured in the system through locked collateral. Suppose the borrower decides not to repay their loan. In that case, its credit position will be liquidated, and the collateral will be automatically sold based on an operation through a smart contract. The sold collateral will then cover all processes and costs related to this loan.
Aave has hedge liquidity pools on the Balancer and Uniswap protocols, designed to address liquidity risk. In this way, the protocol seeks to ensure that users can withdraw their funds at virtually any time. In addition, Aave uses an Oracle system Chainlink to collect and update the prices of individual assets.
Flash Loans
Quick loans are the first option for an uncollateralized loan in the DeFi ecosystem. Quick loans are designed so that the user can borrow immediately and easily without entering collateral, provided that the loan is repaid within a single transaction block.
If the loan is not repaid within the transaction block, the entire transaction will be cancelled, and the funds will be returned to the liquidity pool.
The Aave Flash Loan process takes place within a single transaction on the Ethereum blockchain. It relies on the fact that transactions on Ethereum can be returned, thus cancelling all orders if the borrowed capital is not repaid.
Aave Flash Loan consists of three steps:
- The user borrows tokens from one of the Aave loan funds
- The loan parameters are defined and executed on the Ethereum blockchain
- The user must repay the borrowed amount + a fee of 0.09% of the borrowed amount
If the last condition is met, the entire transaction passes and is permanently added to the Ethereum blockchain. If the last condition is not met, the entire transaction is rejected, and all network orders are cancelled (including the first step, where the user borrows from Aave) as if no transaction had ever taken place.
These quick loans are most often used by arbitrage traders to take advantage of short-term price differences of assets on individual stock exchanges and platforms.
Flash loans are a futuristic idea in the decentralised finance sector. These loans are perhaps the greatest invention and benefit of the Aave protocol with enormous potential. Because the code for these loans is open source, other developers can be expected to use it on their alternative platforms in the future.
Aave Arc
In January, the Aave Protocol launched Aave Arc, aimed at institutional investors.
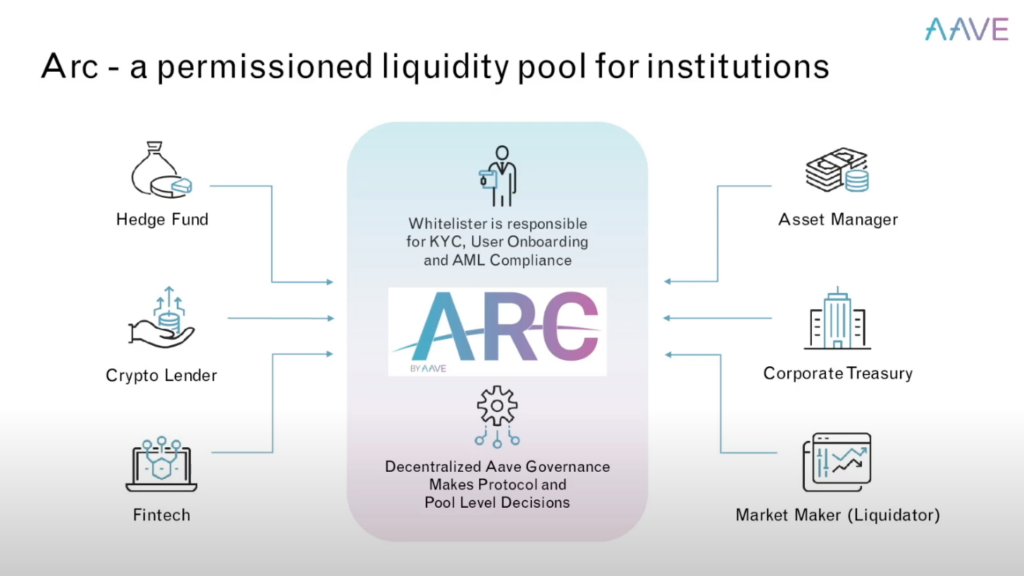
Aave Arc’s goal is to provide institutional investors facing strict regulatory requirements with access to decentralized finance. The Aave Arc protocol uses private liquidity pools to provide institutional investors with direct access to decentralized markets. These pools are separated from the existing liquidity groups on Aave.
The launch of this version for institutional investors has marked a breakthrough in the decentralised finance sector.
“Aave Arc allows institutions to interact with the Aave Protocol the same way any other user would, but on their own separate and permissioned liquidity pool where every user has been verified,” said Stani Kulechov, founder & CEO of Aave for Blockworks.
Native Network Token – Aave
The Aave protocol has its own native token called AAVE. The ETHLend project first sold $LEND tokens through an initial coin offer (ICO), totalling more than $16 million. In October 2020, these tokens were exchanged for current native AAVE tokens at a ratio of 1 AAVE = 100 LEND. At present, the value of one token is more than $90, and the total market capitalization of the tokens exceeds $1.2 billion.
The AAVE token is an Ethereum-based ERC-20 token. There are several powers associated with the ownership of this token. For example, the owners of these tokens have the right to vote on changes and proposals to the Aave Protocol. One token represents one vote.
Aave token can be staked, which means that the storage of the token in the so-called “Safety Module” on the basis of a smart contract ensures an increase in the security and liquidity of the entire protocol. This module works as a kind of decentralised insurance fund, which is designed to secure the protocol against any risky events. For locking these tokens, their owners collect rewards in the form of additional Aave tokens. The remuneration is around the level of 6% p.a.
The Aave token is used to pay fees within the protocol and burned after being used to pay the fees.
The maximum offer of Aave tokens is set at 16 million tokens, while 13.7 million tokens are already in circulation.
Aave – King of DeFi?
Features such as fast loans, switching between variable and fixed interest rates, or a simple and friendly user environment make the Aave protocol the most popular DeFi lending platform today. After all, no government or institution has crowned Aave as such but the users themselves, who have now locked more than $8 billion into the protocol.
Invest With Fumbi Today
If you are considering investing in cryptocurrencies, Fumbi is here for you. Our algorithm-administered portfolio accurately tracks the growth of the entire cryptocurrency market.
Fumbi is the first of its kind to offer cryptocurrencies to the general public, even at small deposits. Investing in cryptocurrencies through Fumbi is very easy and minimises risks.
You can start with a deposit of just €50.
INVEST WITH FUMBIDid you come across a term you didn’t understand? Don’t worry. All essential terms regarding cryptocurrencies are in our Fumbi Dictionary.

 3 min •
3 min •



